Do you want to know how to become a radiation oncologist? Are you interested in a medical career that provides not only patient care but also offers unique opportunities for medical research and a chance to be on the cutting edge of modern medicine
If so, a radiation oncologist career may be the perfect choice for you. In this blog post, I will explain what a radiation oncologist does and how to become one, even if you’re only in high school.
Summary:
- Radiation oncologists specialize in using radiation therapy to treat cancer patients.
- Radiation oncology residency is four years, with the option of fellowship training afterward.
- Going to a top medical school may help a bit. But how you do on your USMLEs (Board) scores and in your med school class ranking will matter more.
- Non-PhD degrees like MBAs and MPHs appear to have no advantage in becoming an oncologist.
Table of Contents
What Are Radiation Oncologists?
Radiation oncologists specialize in using radiation therapy to treat cancer. They diagnose and develop treatment plans for cancer patients, ensuring that the radiation is delivered in the most effective way possible with the least possible side effects.
Radiation oncologists understand how radiation interacts with cells as well as how radiation can target and attack cancer cells while protecting healthy cells. As a result, they can administer radiation treatment to reduce the size of tumors and assist patients with their cancer treatment. A radiation therapist should also be familiar with the latest technology, such as computer-aided treatment planning.
Is a Radiation Oncologist a Doctor?
Are radiation oncologists doctors? The answer to this question is yes; radiation oncologists are doctors.
they learn the different modalities of cancer patient care
A radiation oncologist is a specialized physician who has completed medical school, usually followed by a five-year residency in radiation oncology. During this time, the radiation oncologist trains and gains comprehensive experience on how to use radiation therapy to treat patients with cancer, and occasionally with diseases other than cancer.
Radiation Oncologists vs. Radiation Therapists: What’s the Difference?
Radiation therapists complete 2-4 years of undergraduate education before becoming certified to set up and deliver radiation treatments. A radiation oncologist is a medical school graduate specializing in using radiation therapy and treatment plans to care for cancer patients.
While both radiation oncologists and radiation therapists often work together on patient care, radiation oncologists design the treatment plans for therapists to deliver.
How Long Does It Take to Become a Radiation Oncologist?
Becoming a radiation oncologist takes a lot of work and requires considerable time and energy. But if you’re up to the challenge, the results can be gratifying. It takes at least 13 years after high school to become a radiation oncologist. That includes four years of undergraduate education, and four years of medical school. You will then complete a preliminary year and four years of radiation oncology residency. Along the way, you’ll have to take various standardized exams. These will include the MCAT, the USMLE Step 1, and Step 2 CK.
Undergraduate (4 Years)
The next step is to take the MCAT, a standardized exam. This will test your understanding of biology, chemistry, physics, and psychology. You’ll need to score well on the MCAT for med school acceptance. You’ll have to complete four years of academic and clinical training. The first two years will include anatomy, biochemistry, physiology, pharmacology, and pathology classes. You’ll also have to complete clinical rotations at healthcare facilities. This will give you hands-on experience in specialties ranging from pediatrics to surgery.
Medical School (4 Years)
The next step is to take the MCAT, a standardized exam that measures your knowledge and skills in biology, chemistry, physics, and psychology. You’ll need to score well on the MCAT for med school acceptance.
You’ll have to complete four years of academic and clinical training, which would involve performing medical history, patient examination, and diagnosis of medical conditions. This includes classes in anatomy, biochemistry, physiology, pharmacology, and pathology for the first two years in medical school. You’ll also have to complete clinical rotations at hospitals and other healthcare facilities to gain hands-on experience in specialties ranging from pediatrics to surgery.
Radiation Oncology Residency (5 Years)
After medical school, you’ll have to complete a preliminary year. You’ll then have to match into a radiation oncology residency. To do this, you must take the USMLE Step 1 and Step 2 CK exams. These exams measure your knowledge and skills in the areas of clinical medicine.
Once you’ve passed these exams, you’ll be eligible to apply for residency. A radiation oncology residency is a four-year clinical training program. You will learn radiation diagnostic and therapeutic uses in treating cancer. You’ll also gain experience in patient care.
Fellowship (Optional; Usually 1 – 2 Years)
After your radiation oncology residency, you may pursue further training in a subspecialty. Oncology fellowships allow physicians to gain subspecialty expertise. Fellowship choices include pediatric radiotherapy fellowships, general radiation oncology fellowships, and more. Most oncology fellowships are one to two years. This allows physicians to gain experience and hone their skills in a subspecialty.
After Radiation Oncology Residency: Licensing + Board Certification
Upon completing your residency, you must apply for a medical license. You will need it to practice. You’ll also take certification exams by the American Board of Radiology. While this is optional, some employers find it necessary. Becoming a radiation oncologist takes at least 13 years after high school. It’s a long and arduous process, but if you’re dedicated and passionate, the rewards are worth it.
How Competitive Is It to Become a Radiation Oncologist?
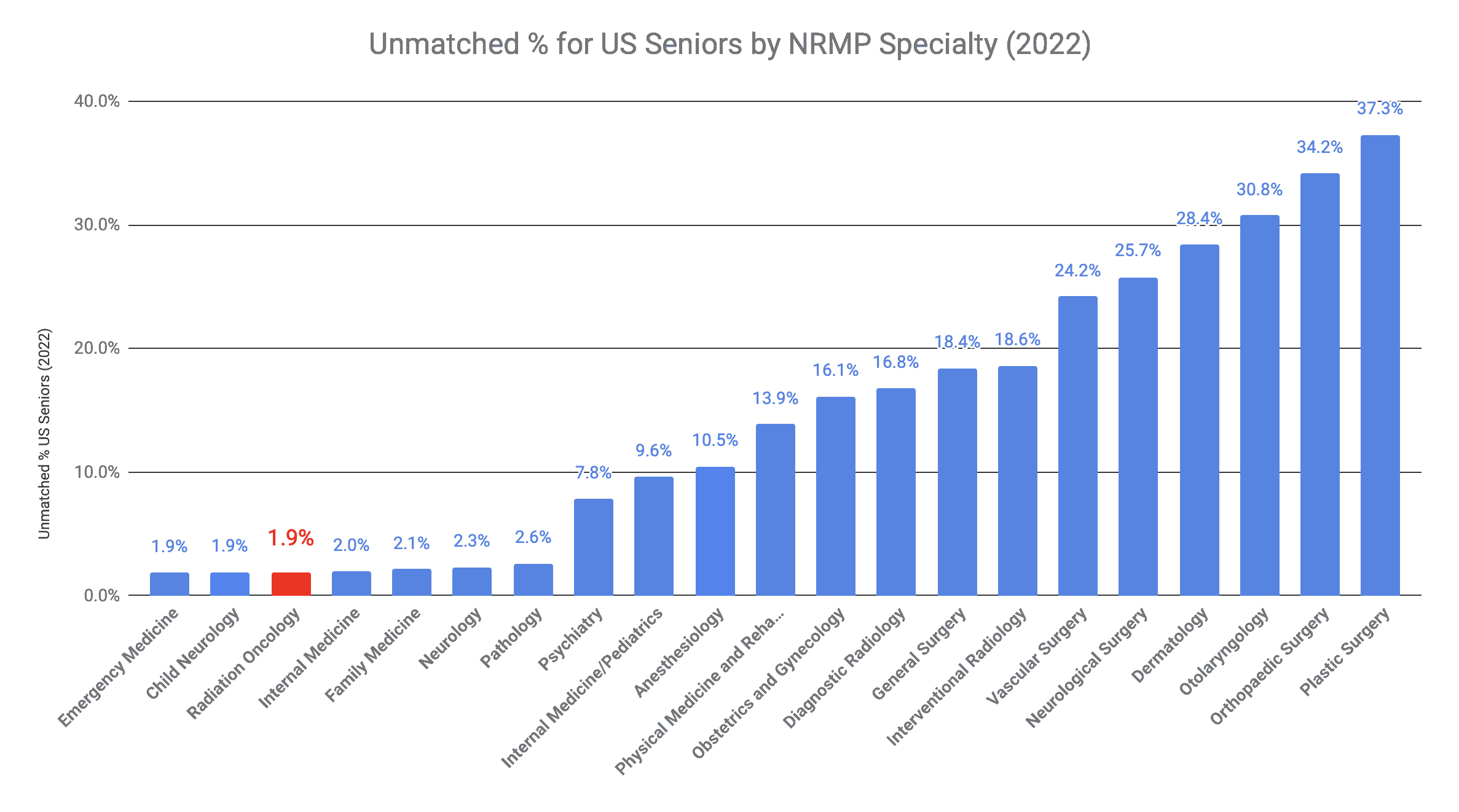
Radiation oncology is one of the least competitive specialties. It was the most competitive specialty at its prime. Increased residency positions have contributed to it becoming a more attainable specialty. Each year, thousands of medical school graduates compete for a position in their preferred specialty. The Match system, run by the National Resident Match Program (NRMP), pairs applicants with training programs based on their preferences.
But how competitive is oncology in the US? To answer this question, it is important to look at the unmatched rates of US seniors by specialty. The unmatched rate refers to the percentage of US seniors who applied for a residency program in that specialty but did not get matched. It considers each applicant’s first-choice specialty. So, if you applied to a different specialty as a “backup” but didn’t match because you matched in your first choice, this wouldn’t count. To learn more about how to maximize your chances at a dream residency through “The Match,” see this article.
In the 2022 Match, graduating US medical school seniors attending MD schools had a 1.9% unmatched rate to radiation oncology. This makes it one of the least competitive specialties.
For more on the competitiveness of anesthesiology relative to other medical specialties, see this article.
Radiation Oncologists’ Annual Compensation
Radiation oncologists have an average annual salary of $394,000. But this can vary dramatically based on practice setting, specialty training, and experience level.
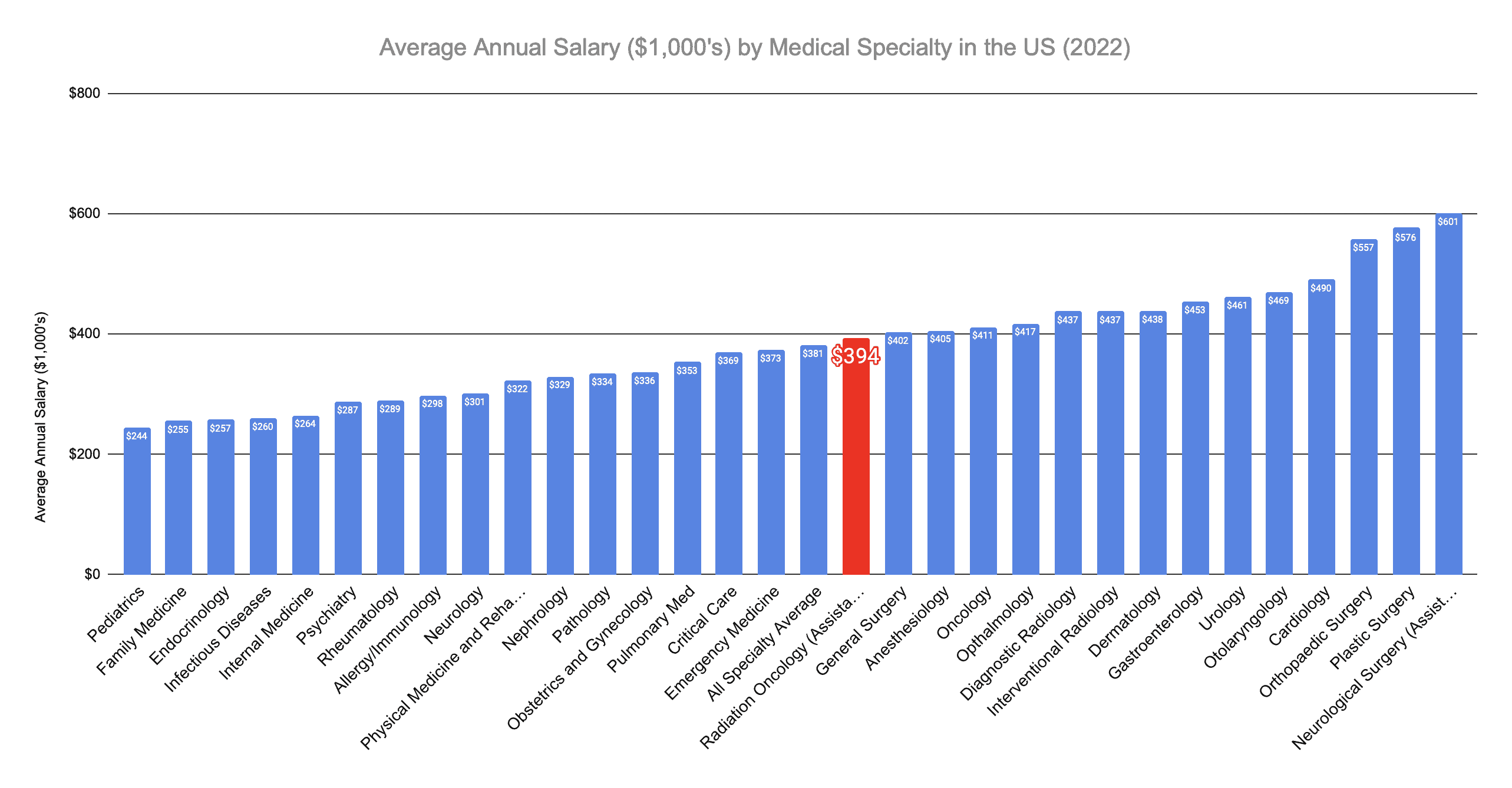
Radiation Oncologists make $394,000 per year on average
How Much Do Radiation Oncologists Make an Hour?
You may also wonder, how much do radiation oncologists make per hour? And how is the balance between time inside vs. outside the hospital for the specialty?
While there isn’t perfect data, we’ve compiled data re: hours/weeks worked and annual salary for various specialties, including radiation oncology.
Here are the data:
| Average Annual Salary | Average Hourly Salary | On-Call Schedule | Hours/Week | Avg Weeks Worked/Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allergy/Immunology | $298,000.00 | $125.93 | 49.3 | ||
| Anesthesiology | $405,000.00 | $146.24 | Medium | 61 | 45.4 |
| Cardiology | $490,000.00 | $177.54 | 57.5 | ||
| Critical Care | $369,000.00 | $114.91 | 66.9 | ||
| Dermatology | $438,000.00 | $211.11 | Low | 45.4 | 45.7 |
| Diagnostic Radiology | $437,000.00 | $170.46 | Low | 58 | 44.2 |
| Emergency Medicine | $373,000.00 | $169.59 | Medium | 46.4 | 47.4 |
| Endocrinology | $257,000.00 | $110.40 | Medium | 48.5 | |
| Family Medicine | $255,000.00 | $101.85 | Medium | 52.6 | 47.6 |
| Gastroenterology | $453,000.00 | $168.53 | Medium | 56 | 47.7 |
| General Surgery | $402,000.00 | $141.88 | High | 59.4 | 47.7 |
| Infectious Diseases | $260,000.00 | $101.44 | High | 53.4 | |
| Internal Medicine | $264,000.00 | $100.81 | Medium | 54.9 | 47.7 |
| Interventional Radiology | $437,000.00 | ||||
| Nephrology | $329,000.00 | $122.40 | Medium | 56 | |
| Neurological Surgery (Assistant Prof. Median) | $600,500.00 | $214.96 | Medium | 58.2 | |
| Neurology | $301,000.00 | $129.09 | Medium | 50.8 | 45.9 |
| Obstetrics and Gynecology | $336,000.00 | $123.26 | Medium | 58 | 47 |
| Oncology | $411,000.00 | $143.43 | Low | 59.7 | |
| Opthalmology | $417,000.00 | $173.97 | Medium | 51 | 47 |
| Orthopaedic Surgery | $557,000.00 | $207.91 | Medium | 57 | 47 |
| Otolaryngology | $469,000.00 | $184.01 | High | 53.1 | 48 |
| Pathology | $334,000.00 | $147.74 | Low | 47.1 | |
| Pediatrics | $244,000.00 | $108.16 | Medium | 47 | 48 |
| Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation | $322,000.00 | $147.76 | 45.4 | ||
| Plastic Surgery | $576,000.00 | $230.77 | Medium | 52 | |
| Psychiatry | $287,000.00 | $131.04 | Low | 46.5 | 47.1 |
| Pulmonary Med | $353,000.00 | $119.77 | Medium | 61.4 | |
| Radiation Oncology (Assistant Prof. Median) | $393,734.00 | $158.36 | Low | 51.8 | |
| Rheumatology | $289,000.00 | $112.33 | 53.6 | ||
| Urology | $461,000.00 | $172.49 | High | 58.1 | 46 |
| Total Average | $381,233.35 | $147.44 | 53.9 |
And the estimated physician salary per hour by specialty ( radiation oncology highlighted in red):
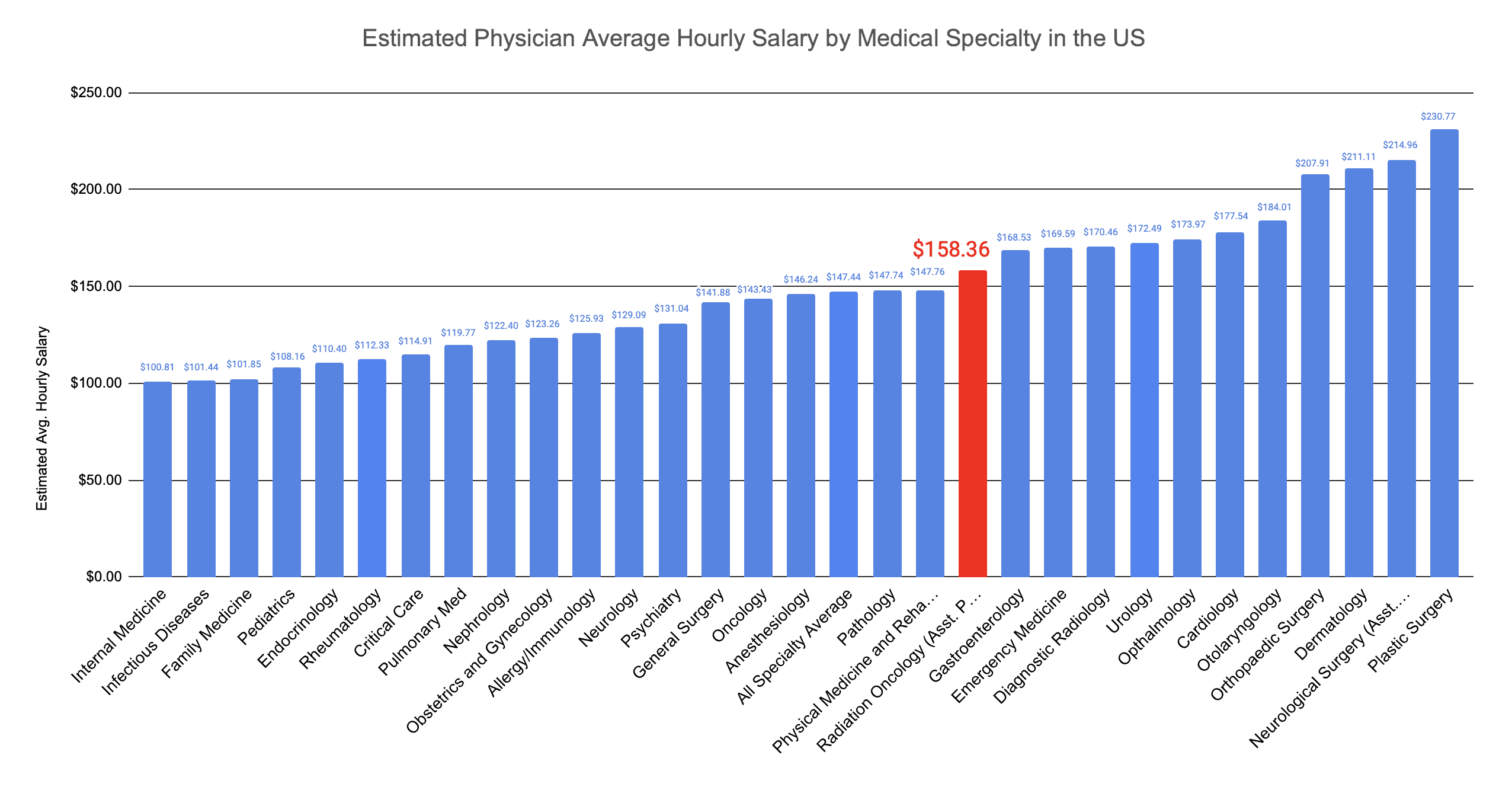
Radiation Oncologists make $158 an hour on average
Note: when data were unavailable for weeks worked per year, we used 48 weeks as an estimate to calculate the estimated hourly salary.
Getting AOA (Med School Honors) Helps in Becoming a Radiation Oncologist
Medical school is one of the most challenging aspects of becoming a doctor. Many medical schools have established Alpha Omega Alpha (AOA) branches to recognize top students.
AOA is the medical school honors society for students who excel in their studies. These students must show an exemplary commitment to professionalism and leadership. Each medical school may elect up to 20% of their graduating class to the AOA.
Induction into AOA is a prestigious honor that carries with it a variety of benefits. AOA members may be eligible for special scholarships and fellowships. They can often receive priority consideration for residency positions.
The AOA advantage is notable for the most competitive fields and/or residency programs. The 2022 Match data showed that the match rate for US medical school seniors with AOA membership was 0% greater than that of US seniors without AOA membership in oncology. Membership in the AOA provided a marginal advantage in matching into an oncology residency.
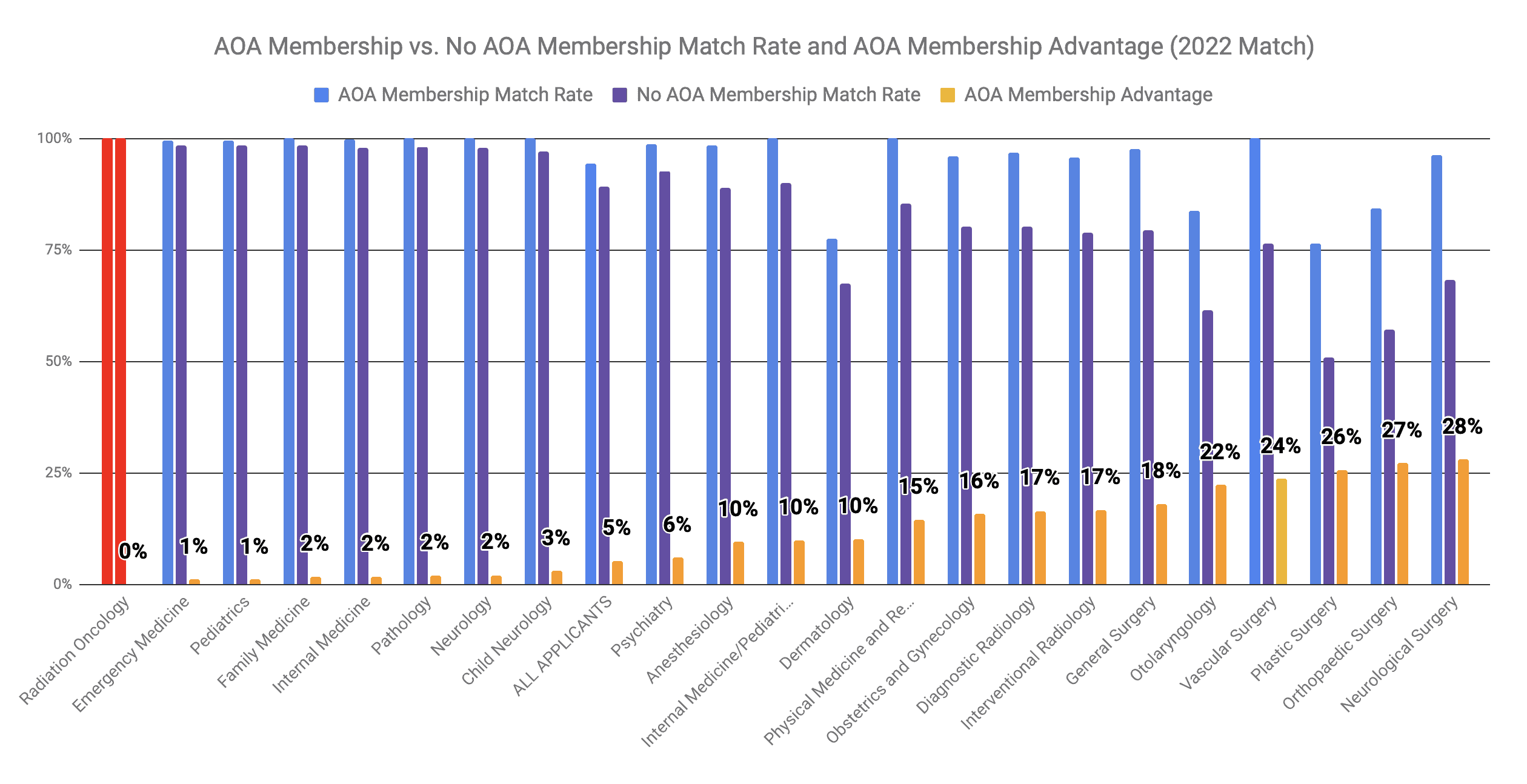
AOA membership correlated with a 0% match rate advantage for Radiation Oncology in the 2022 Match
See this article for more on AOA medical schools and the importance of class rank for matching.
Do You Need to Attend a Top School to Become a Radiation Oncologist?
A top medical school can make a difference when pursuing a career in radiation oncology. According to a survey of program directors, over half of those surveyed reported considering applicants’ med school reputation when considering whom to interview, giving it an importance score of 3.6 out of 5.
Graduating from a school in the top 40 for NIH funding is associated with a -1% increase in the likelihood of matching into oncology as a field. This is because top medical schools have more resources and access to clinical experience. These play a role in helping students prepare for the rigors of the specialty.
That said, it is important to remember that the name of the school alone does not guarantee success in any field. While attending a top medical school may have advantages, it is up to the individual to make the most of the opportunities presented. And while there is an advantage to being from a more prestigious institution, one’s record at the school will matter much more, including things like USMLE scores, class rank, and letters of recommendation.
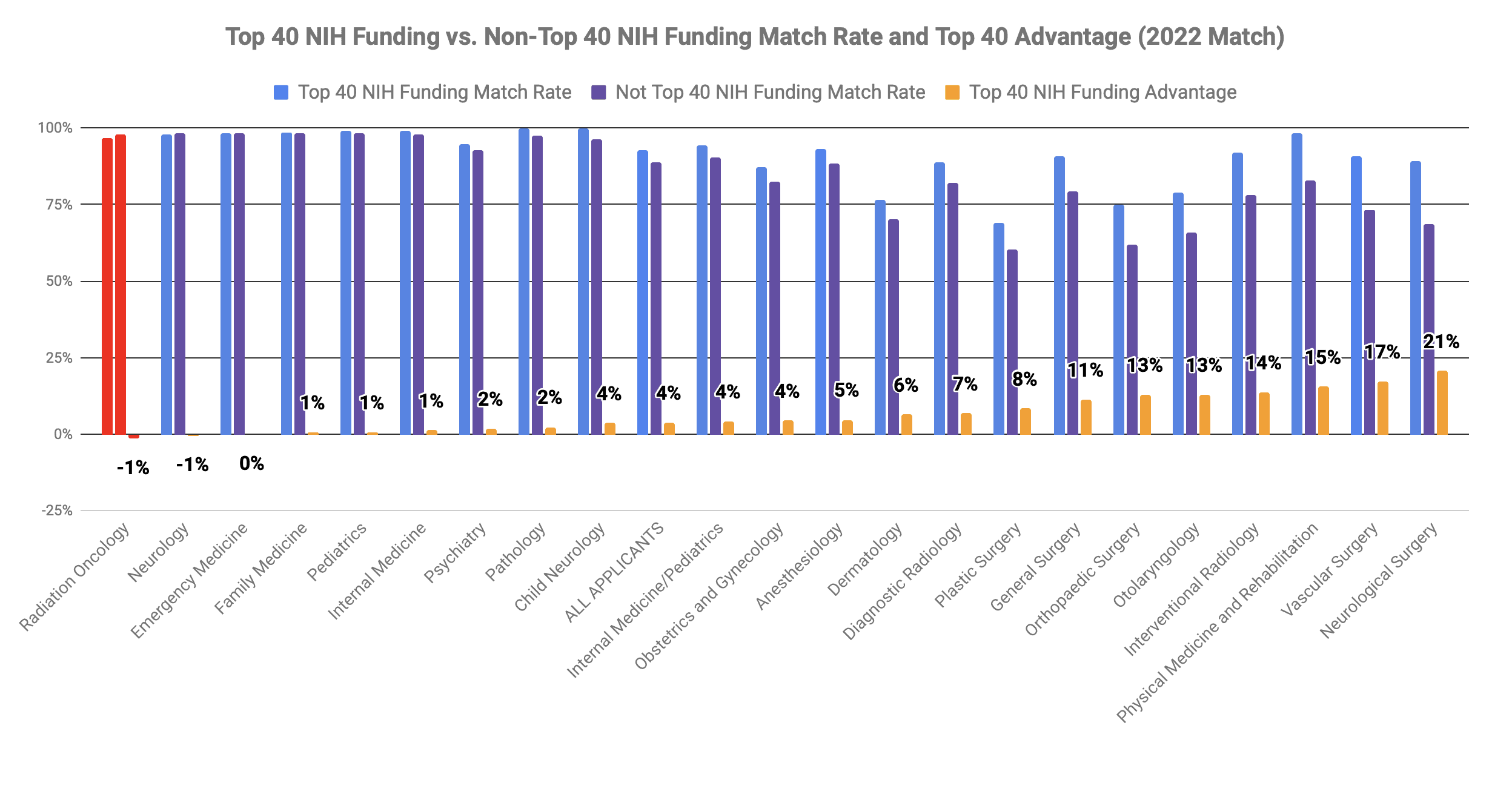
Graduating from a medical school ranked in the top 40 by NIH funding correlated with a -1% match rate advantage for Radiation Oncology in the 2022 Match
Does an MPH or MBA Help You Become a Radiation Oncologist?
Medical training is long and arduous. Many students consider completing other degrees before, after, or even while pursuing their medical studies. Degrees, such as Master of Public Health (MPH) and Master of Business Administration (MBA) may seem attractive to potential oncology residents. But do these degrees give applicants an edge in the residency application process?
Having an extra degree may not matter as much as one thinks. We crunched the numbers on the match rate for graduating students from MD schools for those with non-PhD other degrees vs. those that did not have a second degree. In oncology, the match rate was 0% lower for those with degrees like an MPH or MBA. This implies that having a second degree that isn’t a Ph.D. doesn’t appear to help your chances of matching into radiation oncology.
.
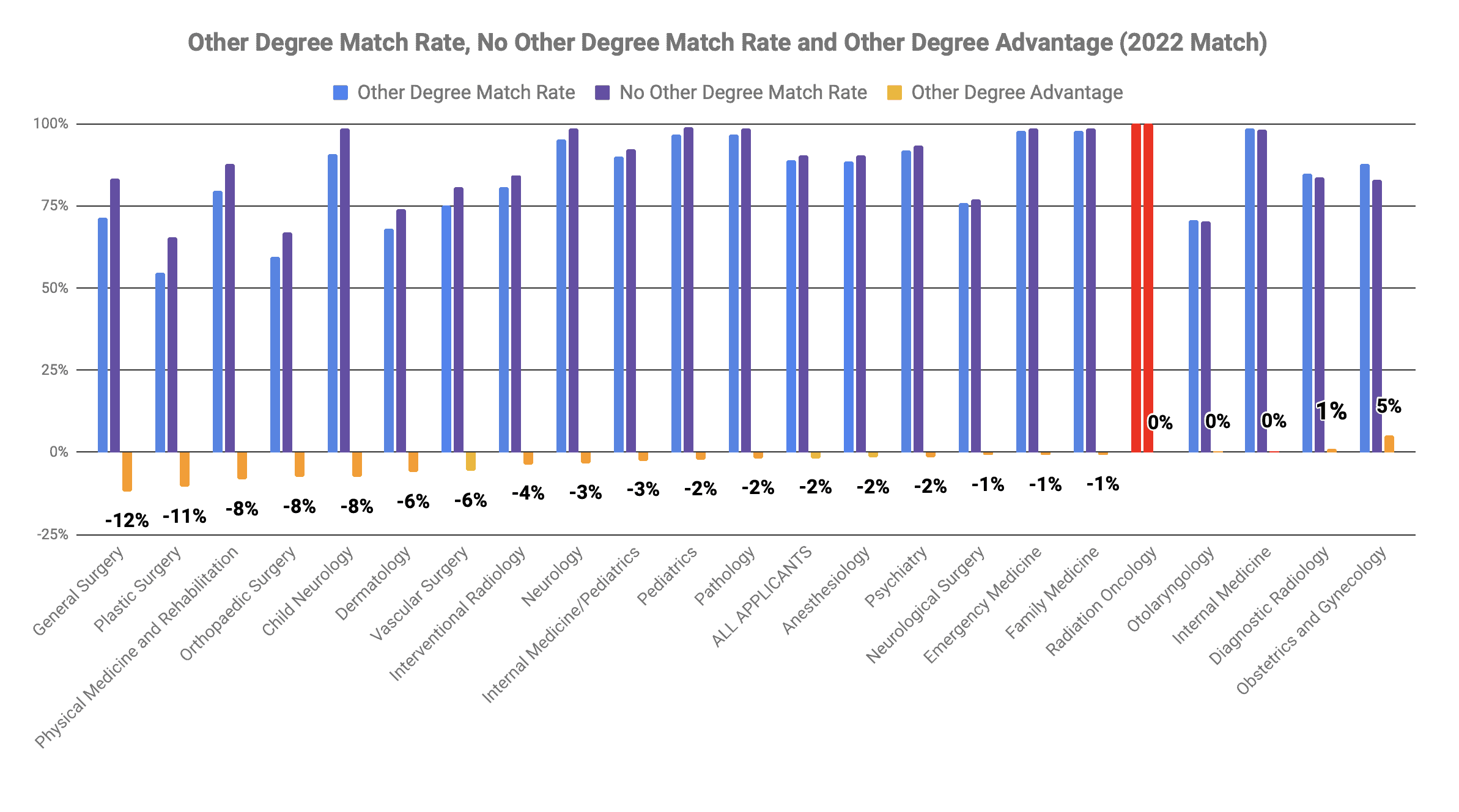
Having another degree like an MBA or MPH correlated with a 0% match rate disadvantage for Radiation Oncology in the 2022 Match
It’s important to note that this study only looked at the match rates of medical students with another degree. The data doesn’t look at the type of degree, the school they got it from, or the quality of the applicant’s experience and credentials.
Having a second degree could open up some career opportunities. For instance, having an MPH or MBA may prove beneficial for those looking to go into healthcare administration or research.
Concluding Thoughts
Becoming an oncologist is a challenging but rewarding career path. It is perfect for those who love pharmacology, physiology, problem-solving and working as part of a team in intense situations. With hard work, dedication, and a desire to help others, oncologists can make a real difference in the world of healthcare.
Looking for an Oncology Residency Advisor?
Looking for an oncology residency advisor? Want help writing your personal statement? Need effective strategies for interviewing? Do you have things on your application – e.g., low USMLE scores, failed USMLEs, no research, IMG status, or others – you need help overcoming?
Be sure to check out our Residency Advisor service.