Cardiology vs. diabetes and endocrinology is one of the debates among medical students interested in physiology. Both specialties allow you to explore the complex workings of the human body and use your skills to improve patient outcomes. However, they also have significant differences, such as the scope of practice, the work environment, and the training requirements.
How do you decide which one is right for you? In this article, we will provide helpful information and tips to help you make an intelligent decision on cardiology vs diabetes and endocrinology and find a fulfilling career that matches your interests and abilities. We will also help you evaluate practical factors such as job availability, salary, and training duration.
Cardiology vs. Diabetes and Endocrinology: Salary and Job Security
Cardiology might be your specialty if you want to earn a lot of money and have a steady demand for your services. But be prepared for a competitive job market after fellowship, even if you graduate from a prestigious program. A Harvard-MGH fellow once told me, “I’ll consider myself lucky if I find a job in a city I recognize.”
Diabetes and endocrinology, meanwhile, offer more job openings. You can easily find a hospital that needs endocrinologists and diabetologists, and the career outlook is positive, even if the salary is not as high as cardiology. However, diabetes and endocrinology also come with some challenges, such as higher burnout and less job security, which we will discuss later.
According to recent data, cardiologists earn an average annual salary of $507,000, while endocrinologists and diabetologists have a considerably lower average salary of $267,000. Of all medical specialties, only orthopedists and plastic surgeons have higher average annual salaries than cardiologists, with orthopedists earning $573,000 and plastic surgeons earning $619,000.
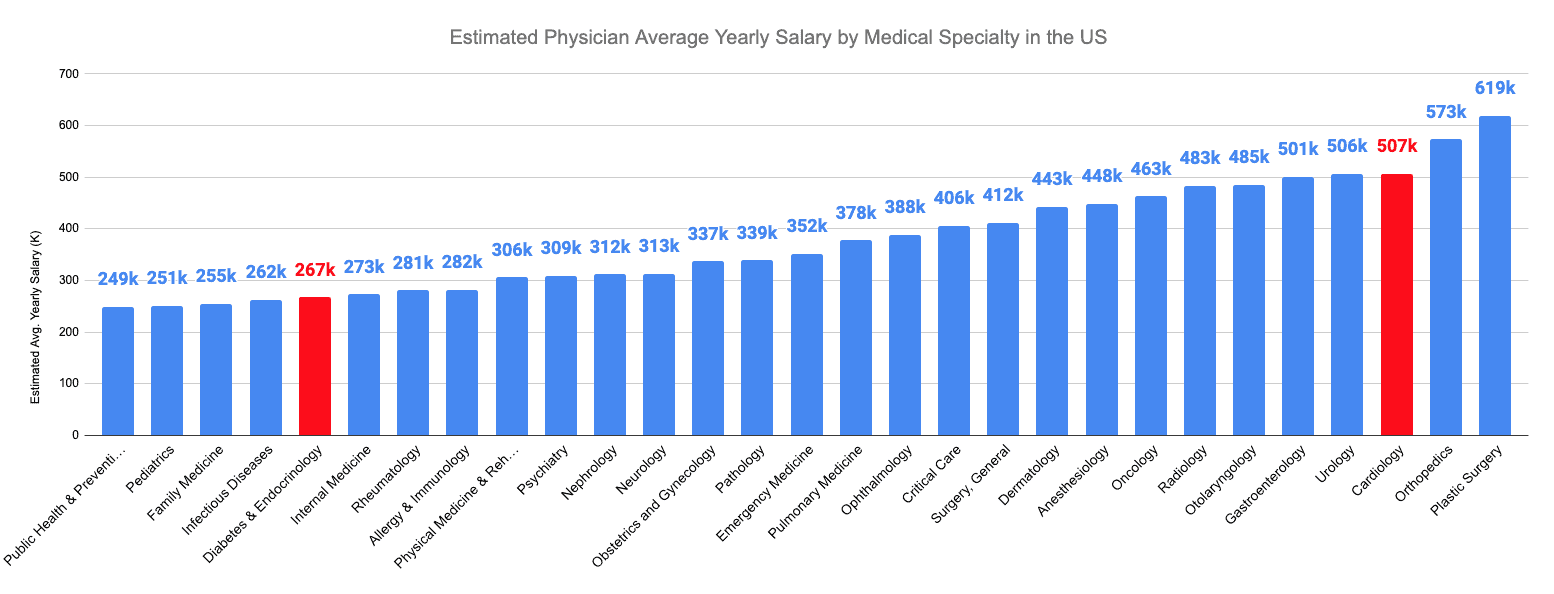
Cardiologists earn $507,000 per year on average, while endocrinologists and diabetologists earn less with $267,000 annually
Cardiology vs. Diabetes and Endocrinology: Competitiveness
Here we can assess the competitiveness of a specialty by looking at the unmatched rate – the % of people who apply and do not match into their preferred specialty.
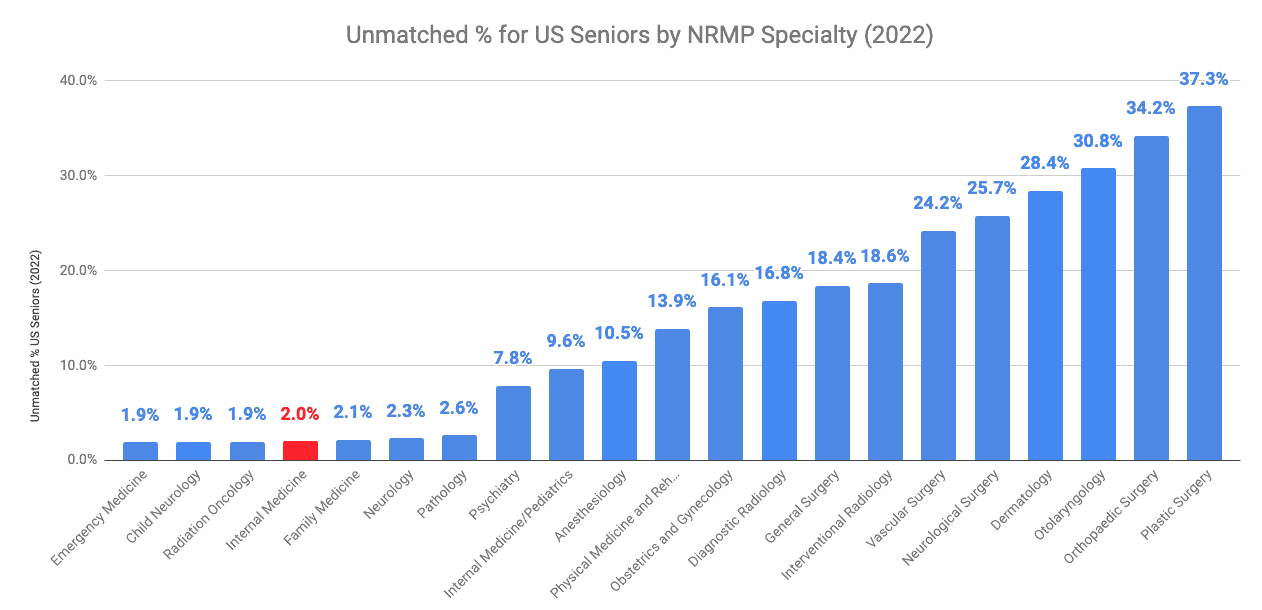
To pursue a career in cardiology or diabetes and endocrinology, you must first match into an internal medicine residency. Among US Seniors, the unmatched percentage for internal medicine residency was only 2%, making it less competitive than other residencies. However, this does not mean that cardiology or diabetes and endocrinology is less competitive. After completing your internal medicine residency, you will still need to match into a fellowship, which is generally more competitive than matching into a residency.
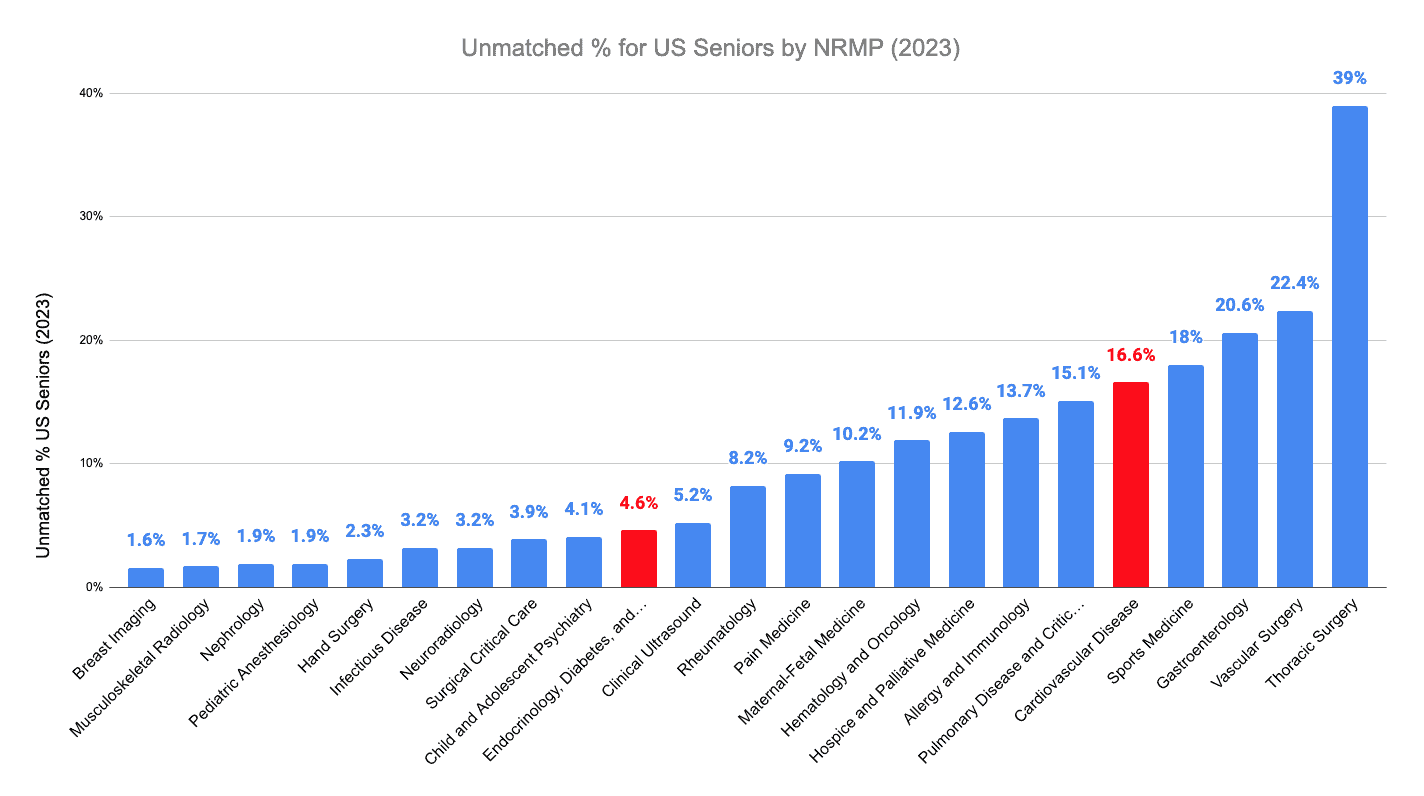
Below is the unmatched percentage among non-pediatric fellowships with >100 applicants. The unmatched percentage of US Seniors applying to the cardiovascular diseases fellowship was 16.6%, making it highly competitive compared to most fellowships with >100 applicants. In comparison, the unmatched percentage of US seniors applying to diabetes and endocrinology was 4.6%, making it less competitive than the cardiovascular diseases fellowship.
Training Path: Fellowship vs. Residency
The training pathways for cardiology and diabetes/endocrinology are quite similar. To become a cardiologist, you must complete a three-year residency in internal medicine, followed by a cardiology fellowship. Similarly, to become an endocrinologist and diabetologist, you must complete a two-year fellowship in endocrinology after completing an internal medicine residency.
A diabetes and endocrinology fellowship is generally less competitive than a cardiology fellowship. Your USMLE scores, med school, and research are the main things for residency applications. Research is also a big thing for fellowship applications, and your residency program counts more, but your USMLE scores matter much less.
Cardiology vs. Diabetes and Endocrinology: Work-Life Balance
Work-life balance is a crucial factor for many medical professionals. Endocrinologists and diabetologists often enjoy a better work-life balance due to the nature of their work. They usually have predetermined working hours, leading to more predictable schedules. However, it’s worth mentioning that this also means endocrinologists and diabetologists are thought to be more easily replaced, as they don’t typically maintain a panel of patients like their cardiology counterparts.
Cardiology, an often patient-centric specialty, requires building long-lasting patient relationships. While this can be rewarding, it also means carrying a patient panel and more administrative work.
That being said, cardiologists work an average of 56.2 hours/week, ranking third after general surgeons and intensivists who work 57.4 and 57.7 hours, respectively. Diabetes and endocrinology ranked near the middle of medical specialties, with an average of 48.9 weekly working hours.
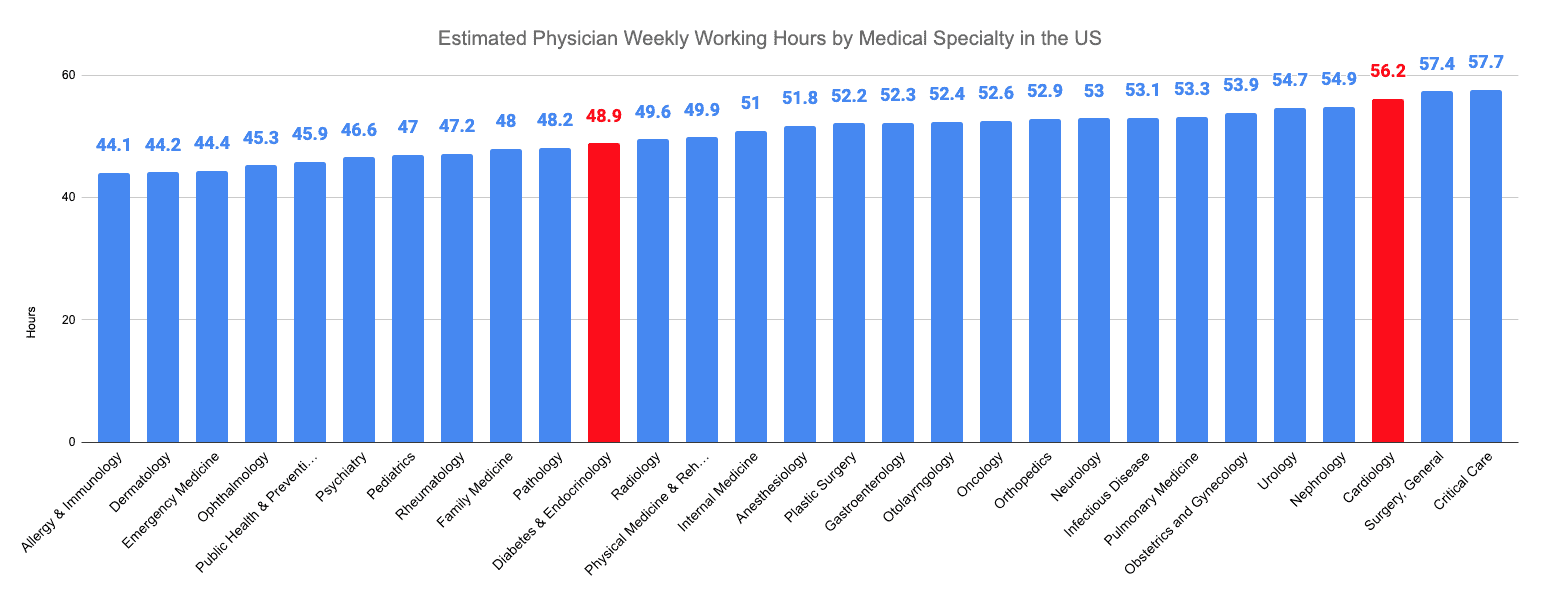
Cardiologists work an average of 56.2 hours per week, while endocrinologists and diabetologists work fewer hours, at 48.9 per week.
Both cardiologists and endocrinologists spend an average of 16 hours per week on administrative tasks and paperwork due to increased diagnostic tests and referral notes.
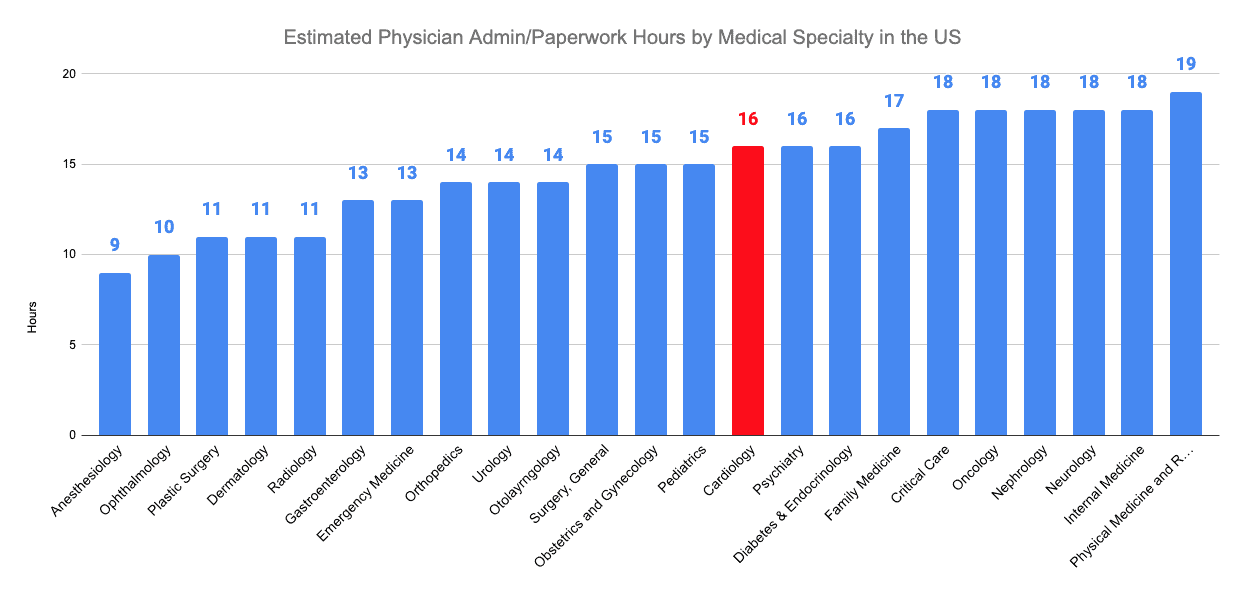
Cardiologists work on admin/paperwork an average of 16 hours per week.
Training Duration and Subspecialties
The training duration is a key aspect to consider when choosing between cardiology vs. diabetes and endocrinology. Diabetes and endocrinology require a minimum five-year training period, including three years of internal medicine residency. On the other hand, cardiology has a minimum of six years of training, including three years of internal medicine residency.
In addition, cardiologists often pursue more subspecialty training in fields like echocardiography or electrophysiology because of the scarce job opportunities. This can increase the length of your cardiology training.
Cardiology vs. Diabetes and Endocrinology: Job Satisfaction and Burnout Rates
Job satisfaction plays a significant role in career fulfillment. According to various studies, cardiology tends to have higher job satisfaction rates than diabetes and endocrinology. Many cardiologists express contentment with their career choice and would choose it again if given the chance. Additionally, cardiology has lower reported burnout rates than diabetes and endocrinology.
According to recent data, cardiology ranked near the upper end of all medical specialties with 93% of cardiologists stating that they would choose the same specialty again. In comparison, diabetes and endocrinology ranked slightly lower with 85% of endocrinologists and diabetologists feeling the same way.
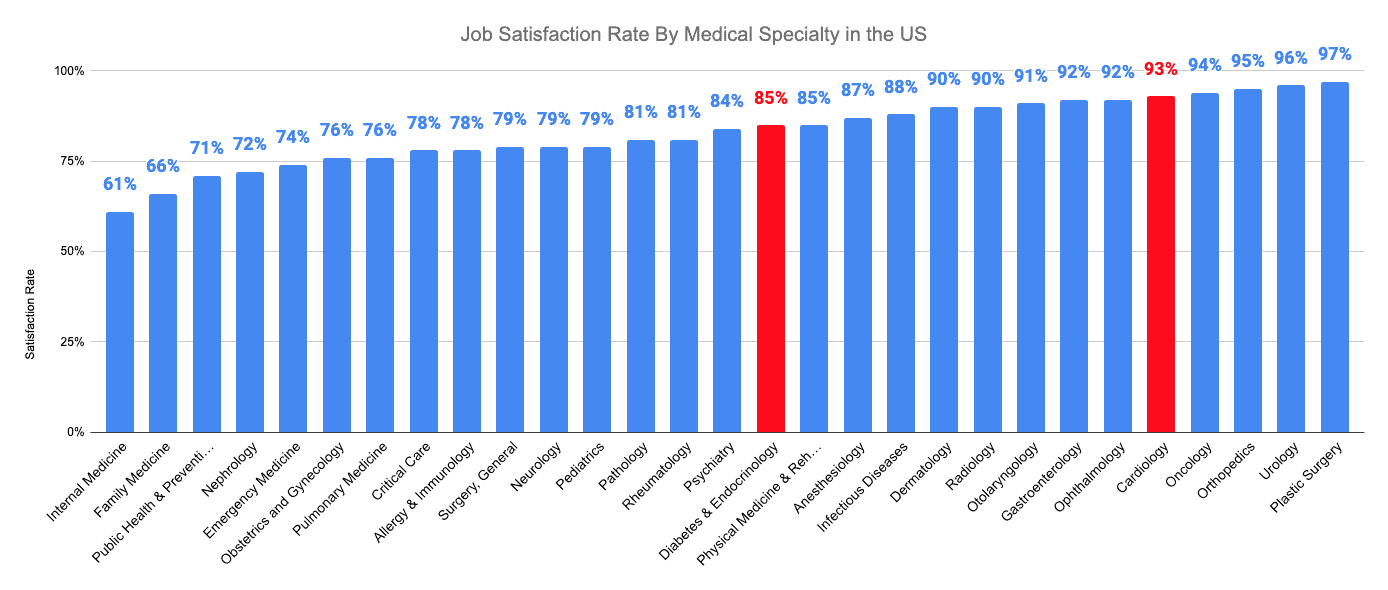
Cardiologists reported a 93% job satisfaction rate, while endocrinologists and diabetologists reported slightly lower satisfaction with 85%
That being said, the burnout rates for cardiology were 43%, near the lower end of all medical specialties. On the other hand, diabetes and endocrinology reported a higher burnout rate of 51%, ranking near the middle of all medical specialties.
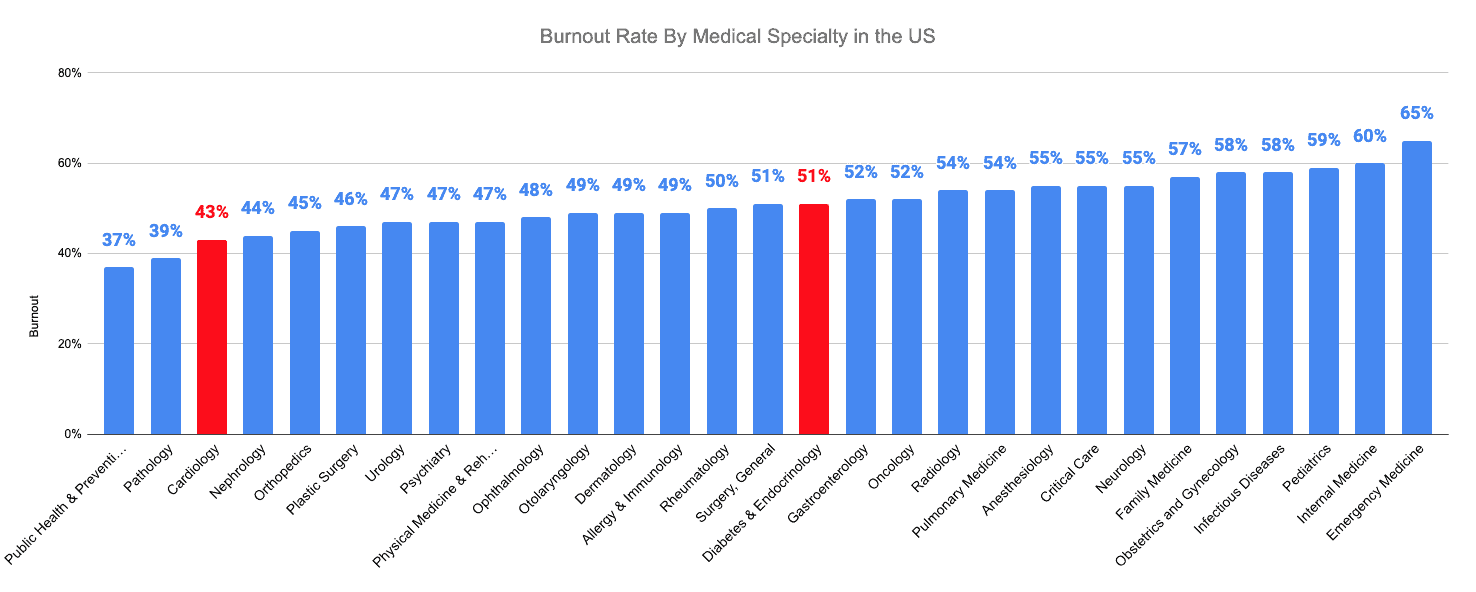
Cardiologists have a burnout rate of 43%, while endocrinologists and diabetologists have a higher burnout rate of 59%.
Cardiology vs. Diabetes and Endocrinology Comparison
To provide a visual overview, here’s a table comparing cardiology and endocrinology:
| Aspect | Cardiology | Diabetes and Endocrinology |
|---|---|---|
| Average Salary | Generally high income due to specialization, especially in interventional cardiology | Lower than cardiology |
| Job Security | High demand due to an aging population and the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases | High demand due to increasing rates of diabetes, hormone-related disorders, and other endocrine conditions |
| Training Path | Typically involves 3 years of internal medicine residency followed by a 3-year cardiology fellowship | Typically involves 3 years of internal medicine residency, and 2-3 years of endocrinology fellowship |
| Lifestyle | Varied; may involve on-call responsibilities, long working hours, and outpatient clinic duties | Regular working hours, but may also involve on-call duties and emergency consultations |
| Administrative Paperwork | High documentation requirements such as notes, test orders, and referral letters | High documentation requirements due to extensive diagnostic and follow-up tests |
| Job Satisfaction | Generally high but can vary with the work environment and patient outcomes | Lower |
| Burnout Rates | Relatively low | Higher |
| Personality | Strong analytical skills, attention to detail, ability to handle stress and pressure | Strong problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and ability to manage complex and chronic conditions related to hormones and metabolism |
Please note that this table serves as a general comparison. To determine the most suitable career for you, consider your personal and career priorities and goals.
Concluding Thoughts
Choosing the right specialty between cardiology vs. diabetes and endocrinology depends heavily on your priorities. To determine this, try reverse engineering your ideal life and identify your top priority. A helpful exercise is to write down the top five things you want to achieve in your career and personal life. Knowing these priorities will make finding a career that aligns with them easier. Often, the biggest obstacle is not a lack of knowledge about different fields but a lack of self-awareness about our preferences.